TL;DR –
- This blog is written for electronics students, engineers, lab technicians, manufacturers, educators, and repair professionals who need accurate measurement of inductance, capacitance, and resistance in real-world applications.
- An LCR meter measures L, C, and R by applying a known AC test signal and analyzing impedance, voltage, current, and phase angle instead of relying on simple DC measurement.
- The lcr meter working principle is based on impedance analysis, where resistance and reactance (from inductance or capacitance) are separated using phase relationships.
- By detecting whether current leads, lags, or stays in phase with voltage, the meter accurately identifies and calculates capacitance, inductance, or resistance values.
- The digital LCR meter working principle improves accuracy and speed through digital signal processing, auto-ranging, and frequency selection, making it ideal for modern labs, R&D, and quality control.
Related Blogs –
An LCR meter is a sensitive instrument used to measure inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) by applying an AC test signal and analyzing impedance, phase angle, voltage, and current. Understanding the LCR meter working principle enables engineers, technicians, students, and manufacturers to obtain accurate component measurements for testing, design, quality control, and troubleshooting. Precision is important whether you are testing a capacitor on a PCB, checking an inductor in a power supply, or verifying resistor tolerances in a production process.
A LCR meter is a type of meter created to measure passive components with significantly higher precision than any ordinary multimeter. Although a multimeter can measure the value of resistance and approximately determine the value of capacitance, it cannot analyze frequency-dependent behavior or phase relationships, both of which are required of inductors and capacitors.
What Does an LCR Meter Measure?
We will discuss the working principle but first, it would be appropriate to take a quick review of the three parameters measured.
Inductance (L)
Resistance to varying currents in a magnetic field by storing energy in a component (usually a coil) is known as inductance. It is expressed in henries (H), and very frequency-dependent.
Capacitance (C)
The capacity of a component to store electrical energy in an electric field is called Capacitance. It is expressed in farads (F) and it depends on the frequency, temperature and dielectric material.
Resistance (R)
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current and is expressed as ohms (Ω). Resistance is theoretically frequency-independent, in contrast to inductance and capacitance, but in practice, components exhibit parasitic effects.
All three are measured on an LCR meter, which measures the behavior of a component when it is exposed to an AC signal.
The LCR Meter Working Principle
LCR meter working principle is based on measuring the impedance of a component when it is excited by a known AC test signal. Measuring the reaction of the component to this signal, that is, the value of both voltage and current, and the angle between them, the meter will precisely decide whether the component is a resistor, capacitor, or inductor, and compute its value.
The principle of working of the LCR meter is impedance measurement which enables the instrument to analyze the response of a component to an alternating current (AC) signal.
Impedance (Z) is the total opposition a circuit presents to alternating current. Unlike simple resistance in DC circuits, impedance consists of resistance (R) and reactance (X).
- Resistance (R)
- Reactance (X) from inductance or capacitance
The fundamental relationship is:
- Inductive reactance: XL = 2πfL
- Capacitive reactance: XC = 1 / (2πfC)
By applying a known AC signal and measuring:
- Voltage (V)
- Current (I)
- Phase angle (θ) between them
The LCR meter establishes whether the component is mostly a resistor, capacitor or inductor and calculates it.
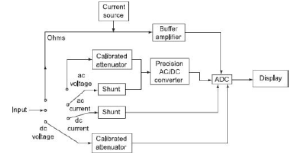
Nvis 9303T Digital LCR Meter – Overview
The Nvis 9303T is a digital LCR meter designed for accurate measurement of passive electronic components like inductors (L), capacitors (C), and resistors (R). It’s typically used in quality control, incoming inspection of components, and automated test systems in industrial and laboratory environments.
Parameter | Frequency | Typical Range (example) |
Capacitance (C) | 1 kHz | 0.1 pF – 9999.9 pF |
10 kHz | 0.01 pF – 999.99 pF | |
Inductance (L) | 1 kHz | 0.1 pH – 9999.9 H |
10 kHz | 0.01 pH – 999.99 H | |
Dissipation / Quality | All | D: 0.0001 – 9.999, Q: 0.0001 – 9999 |
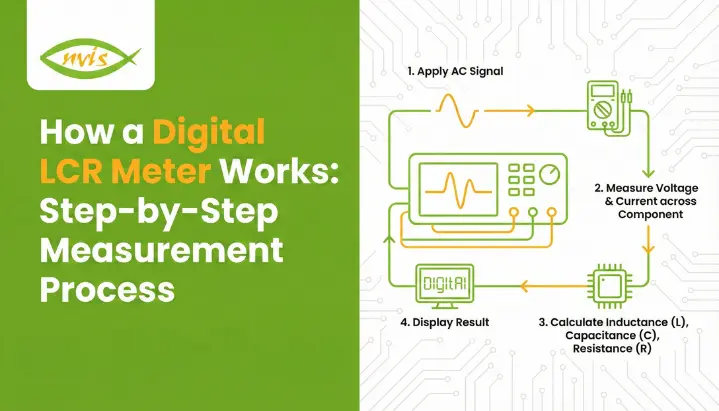
How an LCR Meter Works: Step-by-Step
When the lcr meter working process is divided into a logical sequence the process becomes much clearer. Each step is based on the LCR meter working principle of AC impedance measurement and phase analysis.
1 AC Signal Generation
The LCR meter generates a stable AC test signal using an internal oscillator. Common test frequencies include:
- 100 Hz
- 120 Hz
- 1 kHz
- 10 kHz
Some advanced meters offer selectable or automatic frequency ranges.
2 Applying the Test Signal to the Component
The component under test (DUT) is connected using:
- Two-terminal method (basic measurements)
- Four-terminal (Kelvin) method for higher accuracy
The four-terminal method eliminates errors caused by lead resistance and contact impedance.
3 Measuring Voltage and Current
Precision circuits inside the meter measure the voltage across and current through the component. These measurements form the basis of impedance calculation.
4 Phase Angle Detection
The phase difference between voltage and current reveals the component type:
- 0° phase shift – Pure resistance
- Current leads voltage – Capacitive behavior
- Current lags voltage – Inductive behavior
5 Parameter Calculation and Display
Using digital signal processing, the meter calculates L, C, or R and displays the value on the screen, often along with:
- Quality factor (Q)
- Dissipation factor (D)
- Equivalent series resistance (ESR)
How Inductance, Capacitance & Resistance Are Measured
An LCR meter is an inductance, capacitance, and resistance meter that uses the same basic principle, which is the analysis of AC impedance, but presents the results differently, based on the behavior of the component to the signal applied to it. In this section, the extracting principle of each parameter is detailed according to the lcr meter working principle.
How Resistance (R) Is Measured
When a purely resistive component is tested:
- Voltage and current remain in phase (0° phase angle)
- There is no reactive component (no energy storage)
- Impedance is equal to resistance
The LCR meter calculates resistance using:
- R = V / I
The meter uses an AC signal even in measuring resistance. This enables it to sense parasitic inductance or capacitance which a DC multimeter would not, and makes the measurement more realistic of actual parts.
How Capacitance (C) Is Measured
For capacitors, the current leads the voltage, creating a negative phase angle.
Measurement process:
- The meter applies a known AC frequency
- It measures voltage, current, and phase angle
- Capacitive reactance is calculated:
- XC = 1 / (2πfC)
From this relationship, the meter computes capacitance:
- C = 1 / (2πfXC)
Since the capacitance depends on the frequency and dielectric losses, the LCR meters can be configured to use realistic and application relevant frequencies (usually 100 Hz or 1 kHz).
How Inductance (L) Is Measured
For inductors, the current lags behind the voltage, producing a positive phase angle.
Measurement process:
- The AC signal causes energy storage in a magnetic field
- Inductive reactance is calculated:
- XL = 2πfL
The meter then determines inductance:
- L = XL / (2πf)
Higher test frequencies are often used to improve sensitivity, especially for small inductance values.
Why This Measurement Method Matters
By gauging the behavior of a component under AC conditions, an LCR meter provides:
- More realistic values than DC testing
- Higher accuracy for frequency-sensitive components
- Reliable data for quality control, testing, and design
Inductance, capacitance, and resistance are measured by observing how voltage and current interact under AC excitation, making the LCR meter an essential tool for precise electronic component analysis.
Accuracy Factors in LCR Measurement
Even the best LCR meter requires proper usage to achieve accurate results.
Common Influencing Factors
- Test lead length and quality
- Stray capacitance and inductance
- Component temperature
- Calibration status
High-end meters include open, short, and load compensation to eliminate systematic errors.
Analog vs Digital LCR Meter Working
Feature | Analog LCR Meter | Digital LCR Meter |
Accuracy | Moderate | High |
Ease of use | Manual balancing | Automatic |
Measurement speed | Slow | Fast |
Data display | Scale-based | Numeric + parameters |
Modern usage | Limited | Industry standard |
Due to efficiency and precision, digital models dominate today’s laboratories.
Conclusion
The working principle of an LCR meter is based on a simple yet powerful concept, which involves using a known AC signal and observing the response of a component. Through impedance and phase relation measurements, an LCR meter can accurately measure inductance, capacitance, and resistance, which are important parameters in modern electronics.
Understanding the principles of lcr meter working is not only going to enhance the accuracy of measurements, but also assist the user to identify the correct instrument to use, prevent certain mistakes, and analyze the results properly. With the further development of electronics, tthe digital LCR meter working principle enables faster, smarter, and more reliable component testing of components in education, industry and research.
FAQs
An LCR meter is a device that uses a known AC test signal applied to a component and measures the impedance of the component which is the voltage, current and the phase angle. Based on these values, the meter determines whether the component behaves as a resistor, capacitor, or inductor and calculates its precise value.
Inductance and capacitance are its frequency-dependents that cannot be accurately measured by DC. The AC signal enables the LCR meter to measure reactance and phase shift that is needed to calculate the values of L and C.
The series mode applies in cases where resistive losses are the most important (usually when the inductance is small and the capacitors of interest are very low-value), whereas the parallel mode is used where leakage losses or parallel resistance are important (large capacitors).
Since reactance varies with frequency, capacitor and inductor impedance vary with the test frequency. The loss and material properties also change with the frequency, which interferes with the measurement outcomes.
Yes. An LCR meter measures resistance under AC impedance, and therefore is able to take into consideration parasitic inductance and capacitance which cannot be sensed in a DC multimeter, leading to further refined measurements of actual components.