Posted on February 7, 2026
TL;DR –
- This guide is designed for electronics engineers, lab managers, quality control teams, R&D professionals, and educational institutions looking to choose the right LCR meter for accurate and reliable component testing.
- LCR meters are essential lab instruments used to measure inductance, capacitance, and resistance, enabling component validation, quality control, R&D, and failure analysis.
- Compared to basic multimeters, digital LCR meters offer higher accuracy, AC testing at real-world frequencies, automation, and advanced analysis capabilities.
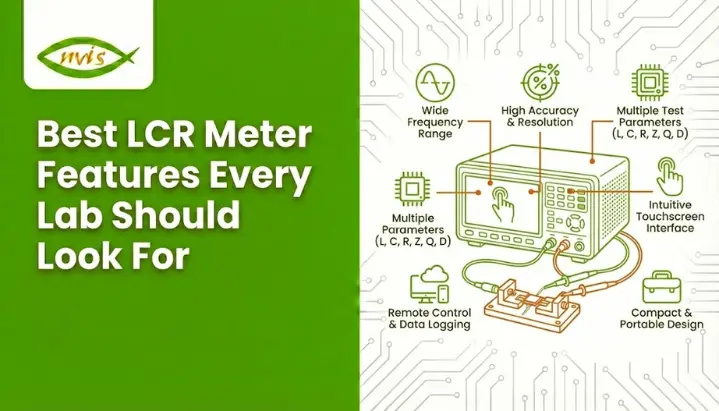
- Accuracy, wide test frequency range, programmable test voltage, fast measurement speed, advanced parameters (ESR, impedance, phase angle), and stable readouts are critical for dependable results.
- The best LCR meter depends on lab needs,high accuracy and advanced features for R&D, speed and repeatability for quality control, and ease of use and durability for educational labs.
Modern electronics laboratories,whether focused on R&D, quality control, manufacturing, or education,rely heavily on precise component testing. LCR meters are one of the most important tools in this ecosystem. They are used to measure inductance (L), capacitance (C) and resistance (R), the basis of characterizing components, troubleshooting, and compliance testing.
Labs can no longer depend on simple instruments as components are smaller, tolerances are tight, and the requirements of the application increase. In particular, the digital LCR meters have changed the way the engineers and technicians would measure, analyze and document the results.However, the wide range of available models and specifications can make selecting the right LCR meter challenging.
Key features of modern LCR meters,such as surface-mount design, large LCD displays, and advanced measurement technology,make them easy to operate, visually refined, and well suited for production-line quality control, incoming component inspection, and automated test systems.
Related Blogs:
- Renewable Energy labs for a global workforce: Aligning education with industry standards
- How Analog and Digital Multimeters Work
- How Practical Labs Make Technical Education and Skilling Industry-Driven
Understanding LCR Meters and Their Role in the Lab
Before diving into features, it’s important to understand what LCR meters actually do and why they are essential.
An LCR meter is a precision test instrument designed to measure:
- Inductance (L) of coils and inductors
- Capacitance (C) of capacitors
- Resistance (R) of resistors and other components
LCR meters use AC test signals at specific frequencies, unlike basic multimeters.This will enable them to test the behavior of components at operating conditions in the real world and not only in the case of DC measurements.
Why Labs Depend on LCR Meters
- Component validation: Ensuring parts meet design specifications
- Quality control: Detecting faulty or out-of-tolerance components
- R&D: Characterizing new materials and designs
- Failure analysis: Identifying degradation, drift, or defects
In modern environments, digital LCR meters have become the standard because they offer higher accuracy, automation, and advanced analysis capabilities.
Types of LCR Meters
LCR meters using a DC based approach to determine capacitance using the RC time constant, including handheld DMMs with capacitance measurement, have a typical accuracy of approximately ±1% of their capacitance. Handheld digital LCR meters are portable and convenient, making them suitable for on-site testing and field maintenance. Benchtop LCR meters typically offer programmable test rates, high measurement accuracy (often up to 0.01%), computer control, and advanced automation features and are commonly used in calibration, dielectric measurements, and high volume production testing.
1-Test Frequency
Electronic elements have to be tested with frequencies that are similar to results in field operations. LCR meters featuring a wide frequency range and frequency selection which can be programmed give the versatility required by both production and research applications.
Frequencies used commonly are 50/60 Hz, 120 Hz, 1 kHz, 100 kHz and 1 MHz. Programmable-frequency instruments enable users to adjust test settings to real applications or to characterize frequencies in R&D systems to determine suitable operating frequencies and identify potential resonances. In the majority of modern LCR meters, an AC test signal is used and has frequency ranges around 10 Hz to 2 MHz.
2- Test Voltage
Most LCR meters permit AC test voltage to be programmed so that the users can regulate the signal level applied to the DUT. The given output voltage is usually determined under the open-circuit conditions.
There is a source resistance internally, and series connected with the AC output and this yields a voltage drop when a device is connected. As a result, the actual voltage applied to the DUT depends on both the meter’s internal source resistance and the impedance of the component under test.
3- Accuracy and Measurement Speed
LCR measurements are necessarily associated with accuracy and speed of measurement. Greater accuracy implies that the measurement times are usually increased whereas faster measurements can limit precision. In order to overcome this trade-off, most LCR meters provide a variety of measurement speed options – often slow, medium and fast.
Depending on the need of the DUT, users have the opportunity of choosing the right mode. Other features that may be used to improve accuracy include averaging and median filtering but these increase the time of the measurements. Specifications of accuracy should be checked in the instrument manual because the general measurement accuracy depends on the frequency, the test voltage and the DUT impedance.
4- Measurement Parameters
Although inductance ( L ), capacitance ( C ), and resistance ( R ) are the most important parameters of measurement, they do not completely describe passive components. Secondary parameters like conductance (G), susceptance (B), phase angle (θ) and equivalent series resistance (ESR) are more insightful into the electrical performance of parts, sensors and materials.
LCR Meter Features Every Lab Should Look For
- Large LCD with backlight: Ensures clear visibility of measurements, even in low-light lab environments.
- Easy operation with strong functions: Allows users to perform accurate measurements quickly without complex setup.
- SMT surface-mount technology: Improves durability, reliability, and overall instrument performance.
- Fast measurement speed (80 ms): Enables quick testing, increasing efficiency in production and quality control.
- Good readout stability: Delivers consistent and repeatable measurement results.
- Dual output impedance (30 Ω, 100 Ω): Provides flexibility to match different components and testing requirements.
Core LCR Meter Capabilities Every Lab Should Look For
The LCR meter that should be sought by every laboratory should be able to give precise and consistent measurements of inductance, capacitance and resistance elementary in order to have trustworthy component testing. It ought to be operated with an AC test signal over appropriate frequencies to enable components to be tested in realistic working conditions as opposed to DC tests. Easy display readability, measurement stability, and high response time are needed to enable effective daily testing.
Moreover, the current digital LCR meters are expected to have convenient design and include technical options, like programmable frequencies, automation, and connection to the data. These features assist the laboratories in simplifying the quality control, enhance the productivity, and also aid in the advanced research, thus the LCR meter is also a necessary tool in the R&D, production, and inspection units.
Measurement Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy is the single most important feature to evaluate when selecting LCR meters.
Why Accuracy Matters
Even small measurement errors can lead to:
- Incorrect design decisions
- Component mismatches
- Product failures in the field
High-quality LCR meters specify accuracy as a percentage of reading plus counts. For professional labs, higher accuracy directly translates to confidence in results.
What to Look For
- High base accuracy across L, C, and R measurements
- Excellent repeatability
- Minimal drift over time
Digital LCR meters typically outperform analog models by providing consistent, repeatable results with minimal operator influence.
Support for Advanced Measurement Parameters
Basic measurements of inductance, capacitance and resistance are necessary but within most laboratories more detailed understanding of the behavior of the components is needed. More detailed electrical characterization of components is given by such advanced measurement parameters as equivalent series resistance (ESR), DC resistance (DCR), impedance and admittance and phase angle with dissipation factor.
The parameters are particularly important when working with power electronics, high-frequency circuits and reliability, when the performance in different conditions should be accurately measured. Digital LCR meters with high end features are able to show more than just one parameter at a time and assist the lab to save time and increase efficiency, as well as provide a more analytical insight.
Connectivity, Automation, and Data Management
There is hardly a case when modern labs work independently. Automated test systems commonly include instruments, which are linked with lab management systems.
Essential Connectivity Options
- USB for local data transfer
- LAN for network integration
- GPIB for legacy automated systems
Benefits of Connectivity
- Automated testing and control
- Seamless data logging
- Easy report generation and traceability
Digital LCR meters with strong connectivity options are ideal for labs aiming to scale operations or comply with documentation standards.
LCR Meter Calibration Stability and Maintenance
The stability of the calibration is a very important aspect of long-term accuracy and reliability of LCR meters. A stable instrument has the same performance over time in terms of measurements and decreases the number of recalibrations and downtimes. Good digital LCR meters have their internal reference components that are stable and designed in a way that they enable these meters to maintain their accuracy even when in constant use.
LCR meters require proper maintenance and frequent calibration to ensure their operation within a given range of tolerances. The ability to perform easy calibration processes, clear documentation, and long calibration intervals also allow laboratories to stay in line with quality standards and reduce maintenance effort and operational costs.
Matching LCR Meter Features to Lab Applications
Not every laboratory has the same testing needs and the best LCR meter will be highly dependent on what it is going to be used for. Appropriate choice of features depending on usage will provide correct results, efficient workflows and better return on investment.
The R&D Labs typically need LCR meters with a broad frequency range, which are able to support higher-level parameters of measurement and a high level of accuracy so that a detailed characterization of the components and experimental studies can be provided.
The advantages of Quality Control Labs include high-speed measurements, high repeatability and strong data logging and reporting options to facilitate large-scale testing and regular inspection procedure.
Educational Labs are designed with ease of use, tough construction and simplicity of displaying results so that students need not spend much time in training and wear and tear of measurement equipment.
Knowing exactly what you will use is one of the ways that you can be certain that you are choosing the LCR meters that will provide the optimal mix of performance, usability and cost without being too complicated or too cheap.
Conclusion:
The choice of the appropriate instrument is not about specifications but rather about the correspondence between the features and the real-life requirements. LCR meters are very important in determining quality of the product, accuracy of design and efficiency of operation.
Accurate measurement, frequency range, sophisticated settings, usability and connectivity can make labs comfortably select digital LCR meters that provide reliable and stable performance presently and flexibility in the future.
Choosing the right LCR meter is not just an equipment purchase,it’s a commitment to precision, efficiency, and excellence in laboratory work.
FAQs
An LCR meter is used to measure inductance, capacitance, and resistance of electronic components for testing, quality control, and research purposes.
Digital LCR meters provide higher accuracy, faster measurements, and advanced features that help labs test components more efficiently and reliably.
A good LCR meter should support a wide frequency range so components can be tested under real operating conditions.
In addition to L, C, and R, LCR meters can measure ESR, impedance, phase angle, and dissipation factor for deeper component analysis.
Choose an LCR meter based on your lab’s needs-accuracy and advanced features for R&D, speed and repeatability for quality control, and ease of use for education labs.








Leave a reply