TL;DR –
- This blog is designed for students, lab instructors, lab assistants, and educators working in electronics, electrical engineering, physics, and applied science laboratories.
- Programmable DC power supplies offer precise voltage and current control, making them ideal for modern student experiments but only when used correctly.
- Following a step-by-step safety procedure (setting current limits first, checking ratings, and enabling output gradually) prevents component damage and accidents.
- Common mistakes like wrong polarity, reused presets, or adjusting circuits while live can lead to serious safety risks and inaccurate results.
- Developing disciplined lab habits and respecting built-in protection features ensures safer learning, reliable experiments, and professional laboratory practices.
Modern student laboratories no longer rely only on basic fixed-output power sources. Electronics, electrical engineering, physics, and applied sciences are growing, and educational institutions are using sophisticated equipment to equip students with practical applications. The programmable DC power supply is one of these vital tools, as it enables controlled and accurate delivery of electrical power to experiments, prototypes, and learning activities.
Although a programmable DC power supply is flexible and more accurate, the way it is used may lead to the destruction of the components, inaccurate outcomes, or even severe safety threats. Laboratories with students especially require a high focus on safe operating practice since in most cases the users are still learning to do it by hand.
This guide explains how to operate a programmable DC power supply safely in student laboratories, covering basic concepts, risk awareness, step-by-step procedures, best practices, and instructor responsibilities. As a student, lab assistant, or an educator, you will find it possible to create a robust safety-first policy regarding laboratory power consumption with the help of this article.
Related Articles
- Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Lab: A Beginner’s Guide to Bench, Programmable & Variable Units
- How Practical Labs Make Technical Education and Skilling Industry-Driven
- Why Your Electrical Training Lab Needs Safety Earthing Training Work Bench Today
What is a programmable DC power supply?
A programmable power supply DC is an electronic instrument used to generate a regulated, adjustable direct current (DC) output. Compared to simple power supplies where the user only operates the power with a manual knob and has only limited control, the programmable units allow users to control voltage and current levels. Many are digitally controlled, and in most cases, the output profile can be stored or automated.
Key Characteristics
- Adjustable voltage and current output
- Digital control and display
- High accuracy and repeatability
- Built-in protection mechanisms
- Suitable for a wide range of experiments
In student laboratories, a programmable power supply DC is commonly used for:
- Circuit analysis and testing
- Semiconductor experiments
- Microcontroller and embedded system projects
- Battery simulation and charging studies
- Research-oriented lab work
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of this equipment is the first step toward safe operation.
Why Safety Matters When Using a Programmable DC Power Supply in Student Labs?
Even though laboratories are established with a controlled learning environment, it should not be assumed that they are risk-free, particularly in cases where electrical equipment is used. Many students are still learning to understand electrical ratings, polarity, and the practical implications of incorrect settings. A programmable power supply DC can provide substantial power and when not used correctly, it can cause serious problems such as damage to delicate electronic components, short circuits and overheating, electrical sparks or burns, and in severe cases, fire hazards.
Student laboratory safety is not about limiting experiments. Rather, it is the empowerment of learning in a form which is responsible and organized. By knowing about possible dangers and applying the safety protocols, students not only decrease the risk of accidents, they also develop confidence, technical skills, and professional laboratory practices that will be highly needed in their academic and industrial settings in the future.
Step by Step Guide to Using a Programmable DC Power Supply Safely in the Lab
A consistent operating protocol must be followed when using a programmable DC power supply in student laboratories to ensure safe, stable, and reliable output. Here is the corrected and expanded step-by-step procedure with the missing safety points added.
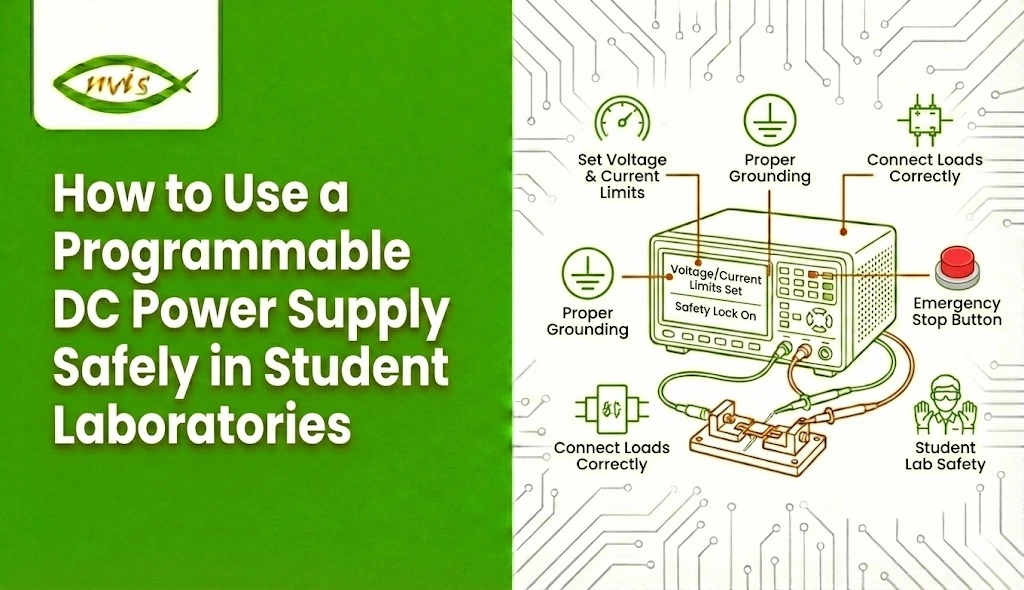
Step 1: Keep the Power Supply OFF
- Never switch ON the supply while connecting or disconnecting a circuit
- Ensure the output is OFF and knobs are at minimum
- Check that cables and probes are not damaged
Step 2: Verify Ratings & Circuit Requirements (Often Missed)
- Confirm required voltage and current from the circuit diagram
- Ensure the supply rating is within safe limits
- Identify correct terminals and channel (if multi-channel supply)
Step 3: Set Initial Parameters
- Set voltage to zero or lowest value
- Set a safe current limit first (component protection step)
- Clear any old preset or stored program settings
Step 4: Connect the Circuit
- Connect with correct polarity (+ to +, – to –)
- Use proper insulated leads – no loose wires
- Tighten terminals securely
- Cross-check wiring with the circuit diagram
- Get instructor/partner verification (recommended in student labs)
Step 5: Enable Output & Power On
- Turn ON the main power
- Then enable the output channel (if separate button provided)
- Increase voltage gradually, not instantly
- Watch voltage/current display while increasing
Step 6: Monitor During Operation
- Observe for abnormal signs:
- Excess current draw
- Overheating components
- Smoke or smell
- Unusual sounds
- Use multimeter/oscilloscope for verification
- Do not touch live terminals or exposed conductors
- Keep liquids and metal tools away
Step 7: Fault Response (Commonly Missing)
- If current spikes or a short is suspected:
- Turn output OFF immediately
- Do not adjust wiring while live
- Let components cool before touching
Step 8: Shutdown Procedure
- Reduce voltage back to zero
- Turn output OFF first, then main power OFF
- Disconnect the circuit safely
- Reset voltage and current knobs to minimum for the next user
Step 9: Post-Use Check (Good Lab Practice)
- Remove leads properly (hold connector, not wire)
- Report any equipment issues
- Leave the bench in safe default condition
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Programmable DC Power Supply
- Setting voltage before current limit
Always set the current limit first. If voltage is applied without a defined current limit, sensitive components can burn out instantly during a short or overload condition. - Forgetting to turn output OFF before wiring
Never connect or modify circuit wiring while the output is ON. Live connections increase the risk of short circuits, sparks, and component damage. - Reusing previous presets or stored settings
Programmable supplies can retain earlier configurations. If not cleared, old voltage/current values may be applied unexpectedly and damage the new circuit. - Wrong polarity connections
Reversing positive and negative terminals can permanently damage components like ICs, LEDs, and microcontrollers. Always double-check polarity before enabling output. - Jumping directly to the required voltage
Increasing voltage too quickly prevents you from spotting abnormal current draw early. Always raise voltage gradually while watching the display readings. - Ignoring current spike warnings
Sudden current spikes usually indicate a wiring error or short circuit. Turn the output OFF immediately and inspect the setup before continuing.
Best Practices for Students
The safe use of a programmable power supply DC is not just about producing rules and memorizing them, but is also assisting the students to form professional laboratory habits. Students must be able to think with caution, as they need to always read through the instructions of the experiment, ensuring that the necessary level of voltage and current is taken. It is better to start with low settings and raise the settings gradually to minimize the chances of a sudden failure of the components or the destruction of the circuits.
The protective features built into a programmable DC power supply should never be bypassed, as they are designed to prevent accidents and equipment damage. In case of uncertainty, students need to seek the advice of a lab instructor or assistant as opposed to making assumptions, both to prevent unsafe operation and inaccurate results of an experiment.
Conclusion
A programmable DC power supply is both a valuable and necessary instrument in modern student laboratories. It is flexible, precise and highly featured, and therefore suitable in the educational context, but only when it is used properly.
Through the knowledge of voltage and current control, adhering to the organized operating rules and the consideration of in-built protective measures, students are able to operate a programmable power supply DC with utmost safety and responsibility. In their turn, teachers and laboratory managers are critical to providing support to safe practices and keeping equipment up to standards.
After all, safety does not inhibit learning, it is the backbone, upon which experimentation, innovation, and discovery can be successful in student laboratories.
FAQs
A programmable DC power supply is a laboratory instrument which provides regulated DC current and voltage. This enables the user to accurately adjust the power output and is good in student experiments, testing circuits and learning electronics in a controlled and safe manner.
Yes, students may be able to work with a programmable power supply DC safely in case they follow instructions in the lab, establish appropriate limits, and operate under supervision. Experiment safety is also minimized through inbuilt safety features.
Prior to its activation, verify voltage and current settings, check cables, check polarity and maintain a clean and dry workspace. These inspections assist to avoid short circuiting and equipment destruction.
The rise in voltage is gradually applied to the circuit to enable students to observe the behavior of the circuit and avoid sudden overloads. This is done to provide protection on sensitive parts and to enhance safety in case a programmable power supply DC is used.
Current limiting is the setting that limits the current fed to a circuit. It safeguards against overheating, short circuiting, and failure of components and so the programmable power supply DC is safer in the use of the student laboratory.